
Curiosities of nature
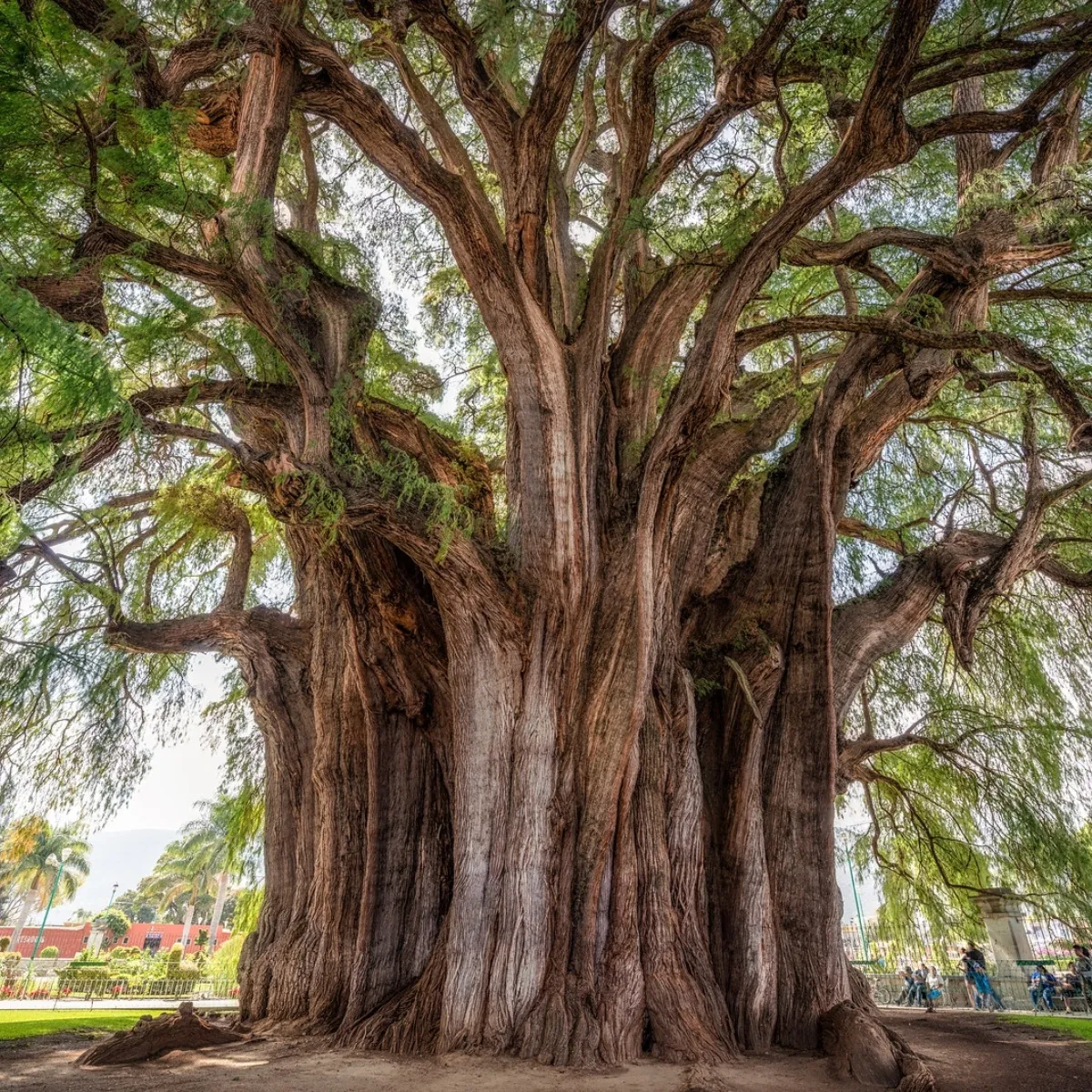
The Tule Tree in Oaxaca, Mexico
In Oaxaca, Mexico, there is one of the trees with the largest trunk circumference in the world. The Tule tree, as it is known, exudes fullness at its nearly 2,000 years of age since, according to legend, it was planted in a sacred place. If 10 midsize cars were placed side by side in a circle, this would be about the same size as the circumference of this tree. The species is native to Mexico, although it is also found in very localized areas of southern Texas and northwestern Guatemala. In 1921, to celebrate the centenary of Mexican independence, the species was selected as a national tree for its splendor, beauty, longevity, colossal dimensions, and tradition. Fortunately, its wood is soft and weak, so it is not used for construction.
According to a Zapotec legend, it maintains that it was planted about 1,400 years ago by Pechocha, priest of Ehécatl, god of the wind. Another legend says that some leaders of the great nations met and decided to separate into 4 groups, heading to the 4 cardinal points and in each one they planted ahuehuetes, the great Tule would be one of them. There is a tendency to affirm that its location is a sacred site.

IT MAY INTEREST YOU
 Color the streets pink and white in spring: which is the most beautiful tree in the world and why, according to AI
Color the streets pink and white in spring: which is the most beautiful tree in the world and why, according to AI
Its delicate branches, the soft tones of its petals and the harmonious shape of the tree make it an almost poetic image.
 The South American country that changes construction thanks to an ancient, mega-resistant material: more than steel
The South American country that changes construction thanks to an ancient, mega-resistant material: more than steel
This material that grows in South America creates the most resistant constructions and radically changes the world of architecture One particular building material has been used for millennia by various cultures in South America. This is due to its structural resistance that allows the creation of homes, bridges and shelters. Its archaeological presence shows that it was one of the most valued construction resources in seismic and humid areas.
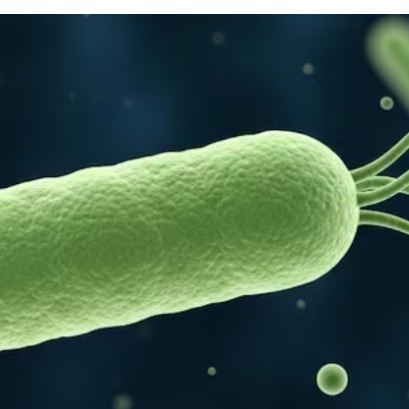 The discovery of methane-producing bacteria in trees rethinks the ecological role of forests
The discovery of methane-producing bacteria in trees rethinks the ecological role of forests
Pioneering study shows trees surprising internal microbial diversity and potential influence on global climate, driving novel strategies for agricultural and forestry management





















